How does a keto diet work? This popular weight-loss strategy flips the script on traditional eating habits, encouraging your body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. The key lies in a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet, forcing your body into a state of ketosis. This metabolic shift can lead to numerous potential benefits, from weight loss to improved blood sugar control, but it’s crucial to understand the science behind it and its potential risks.
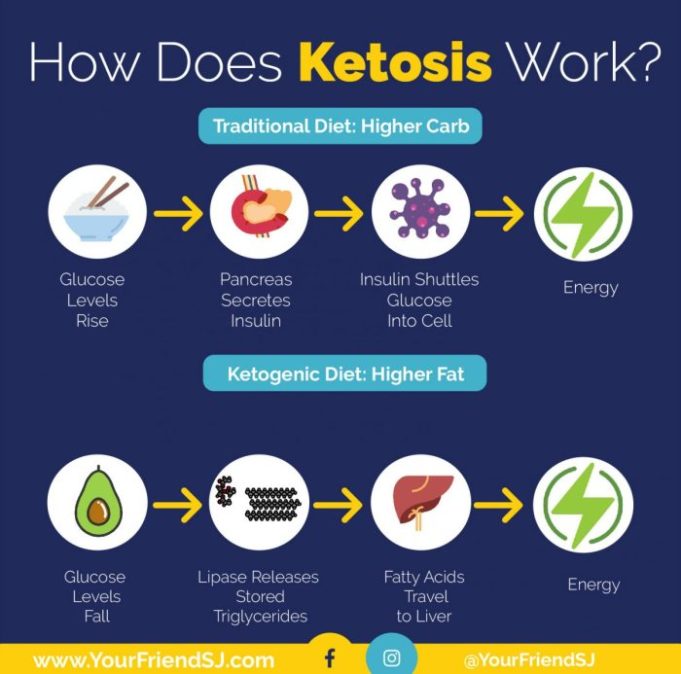
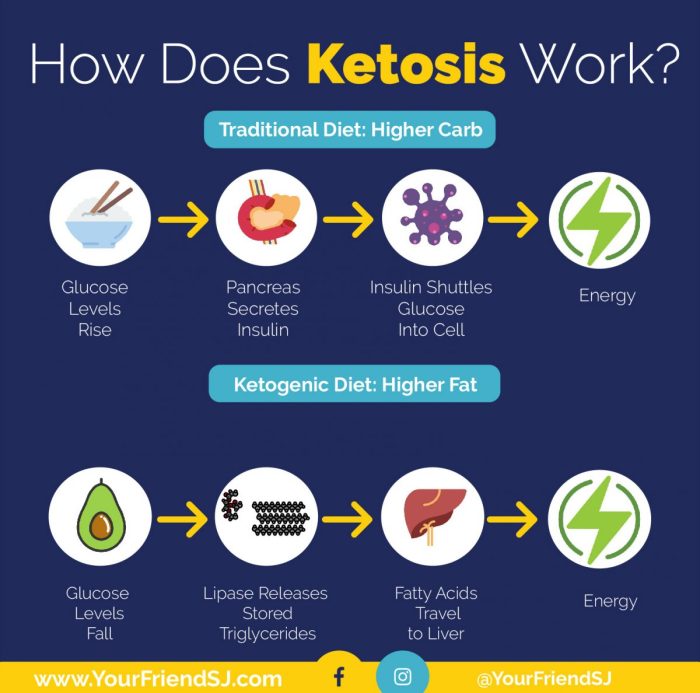
The keto diet is based on the principle of reducing carbohydrate intake to such a low level that your body enters a state of ketosis. In this state, your body begins to break down fat for energy, producing ketones as a byproduct. These ketones then become your body’s primary fuel source, replacing glucose, which is usually derived from carbohydrates. This shift in metabolism can lead to various physiological changes, influencing everything from appetite and energy levels to your overall health.
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet, often shortened to “keto,” is a high-fat, very low-carbohydrate eating plan that forces the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. This diet has gained popularity in recent years as a potential weight-loss strategy and for its potential benefits in managing certain medical conditions.
Understanding Ketosis
Ketosis is a natural metabolic process that occurs when the body doesn’t have enough glucose (sugar) for energy. In this state, the liver converts fat into ketones, which are then used as an alternative fuel source by the brain and other organs. This differs from typical carbohydrate metabolism, where glucose is the primary fuel source.
Macronutrient Ratios in the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is characterized by its strict macronutrient ratios, typically consisting of:
- Fat: 70-80% of daily calories
- Protein: 15-20% of daily calories
- Carbohydrates: 5-10% of daily calories
This high-fat, low-carb approach forces the body to enter ketosis, as it depletes its glycogen stores (stored carbohydrates) and begins burning fat for energy.
How the Keto Diet Works
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that forces the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. This state occurs when the body begins to burn fat for energy instead of glucose, the primary fuel source for most cells. Understanding the science behind the keto diet is crucial to grasping its effectiveness and potential benefits.
The Role of Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin and glucagon are hormones produced by the pancreas that play a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels and energy metabolism. When we consume carbohydrates, our bodies release insulin, which signals cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This process lowers blood sugar levels and provides energy for cellular functions. However, when blood sugar levels drop, the pancreas releases glucagon, which triggers the breakdown of stored glycogen in the liver, releasing glucose back into the bloodstream to raise blood sugar levels.
Inducing Ketosis
The ketogenic diet significantly reduces carbohydrate intake, forcing the body to seek alternative energy sources. When carbohydrate levels are low, insulin levels also decrease, leading to a reduction in glucose uptake by cells. This triggers the release of glucagon, which stimulates the breakdown of fat stored in adipose tissue. Fat is broken down into fatty acids, which are transported to the liver.
Ketogenesis: The Production of Ketones
In the liver, fatty acids undergo a process called ketogenesis, where they are converted into ketone bodies. These ketone bodies, including beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone, are water-soluble molecules that can be used as an alternative fuel source by the brain and other tissues. Ketones provide a readily available energy source when glucose is scarce.
Adaptation to Fat as Fuel
Initially, the body may experience a period of adaptation as it transitions from relying on glucose to using ketones. This period, known as the “keto flu,” can be characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and nausea. However, as the body becomes more efficient at burning fat, these symptoms typically subside. Over time, the body adapts to using ketones as its primary fuel source, leading to increased energy levels, improved mental clarity, and weight loss.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet, with its emphasis on fat intake and restriction of carbohydrates, has gained significant attention for its potential health benefits. While it’s important to note that individual responses can vary, research has highlighted a number of advantages associated with this dietary approach.
Weight Loss
The ketogenic diet’s effectiveness in promoting weight loss is attributed to its ability to induce a state of ketosis. When the body is deprived of carbohydrates, it turns to stored fat for energy, leading to a reduction in body weight. Studies have shown that individuals following a ketogenic diet experience significant weight loss compared to those on traditional low-fat diets. For example, a 2019 study published in the journal *Obesity* found that participants on a ketogenic diet lost an average of 12.3 pounds over a 12-week period, compared to 5.8 pounds lost by those on a low-fat diet.
Improved Blood Sugar Control
The ketogenic diet has demonstrated potential in improving blood sugar control, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the diet helps to stabilize blood glucose levels, reducing the need for insulin and minimizing fluctuations in blood sugar. A 2018 study in the journal *Diabetes Care* found that individuals with type 2 diabetes who followed a ketogenic diet for 12 weeks experienced a significant reduction in their HbA1c levels, a marker of long-term blood sugar control.
Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. The ketogenic diet has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, potentially due to its impact on reducing insulin resistance and improving lipid profiles. A 2017 study published in the journal *Nutrients* found that a ketogenic diet significantly reduced inflammatory markers in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
Benefits for Epilepsy, How does a keto diet work
The ketogenic diet has a long history of use in the treatment of epilepsy, particularly in children. While the exact mechanism is not fully understood, the diet appears to reduce seizures by altering brain metabolism and reducing oxidative stress. A 2019 review article in the journal *Epilepsy & Behavior* found that the ketogenic diet is effective in reducing seizures in up to 50% of children with epilepsy who do not respond well to conventional anti-seizure medications.
Benefits for Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. The ketogenic diet has been shown to improve several components of metabolic syndrome, including reducing abdominal fat, lowering blood pressure, and improving blood lipid profiles. A 2016 study in the journal *Metabolism* found that individuals with metabolic syndrome who followed a ketogenic diet for 12 weeks experienced significant improvements in their blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and waist circumference.
Benefits for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can lead to irregular periods, excess androgen production, and insulin resistance. The ketogenic diet has been suggested as a potential dietary intervention for PCOS, as it may help to regulate insulin levels, reduce inflammation, and improve hormonal balance. While more research is needed, preliminary studies have shown promising results. A 2017 study published in the journal *Nutrients* found that a ketogenic diet improved menstrual cycles and reduced androgen levels in women with PCOS.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of the Keto Diet
While the ketogenic diet can be effective for weight loss and managing certain health conditions, it’s crucial to be aware of its potential risks and side effects. Like any restrictive diet, the keto diet can have short-term and long-term implications for your health.
Keto Flu
The keto flu is a common side effect experienced by individuals transitioning to a ketogenic diet. It’s characterized by symptoms like fatigue, headache, nausea, constipation, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms typically occur within the first few days or weeks of starting the keto diet and are usually temporary. They arise due to the body’s shift from burning glucose for energy to burning fat, a process that can disrupt electrolyte balance.
Constipation
Constipation is another common side effect of the keto diet. This is because the low-fiber intake associated with the diet can slow down digestion. To prevent constipation, it’s essential to drink plenty of water and consume high-fiber foods like leafy green vegetables, broccoli, and avocado.
Nutrient Deficiencies
The ketogenic diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned. Since it restricts fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are rich sources of essential vitamins and minerals, it’s important to supplement your diet or choose nutrient-dense foods to ensure adequate intake.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Electrolyte imbalances are a significant concern with the keto diet. This is because the body loses electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium during the initial phase of ketosis. These electrolytes are crucial for maintaining fluid balance, muscle function, and nerve function. Electrolyte imbalances can lead to symptoms like fatigue, muscle cramps, and dizziness.
Long-Term Health Implications
While short-term side effects of the keto diet are often manageable, long-term implications need to be considered.
- Kidney Stones: The high protein intake associated with the keto diet can increase the risk of kidney stones in some individuals. This is because protein metabolism produces waste products that can form crystals in the kidneys.
- Heart Health: The keto diet’s high saturated fat content can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Bone Health: The keto diet’s low calcium intake can increase the risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Long-term adherence to the keto diet can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, potentially impacting overall health.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a ketogenic diet, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions. Your doctor can assess your individual needs, potential risks, and ensure that the diet is safe for you. They can also help you create a personalized plan that addresses any potential nutrient deficiencies and minimizes side effects.
Food Choices and Meal Planning on the Keto Diet: How Does A Keto Diet Work
The ketogenic diet requires careful food choices and meal planning to maintain ketosis. It emphasizes high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate foods. This section will provide guidance on food choices and meal planning for a successful ketogenic journey.
Sample Ketogenic Meal Plan
A sample ketogenic meal plan for a day can look like this:
| Meal | Food Choices |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | 2 eggs with spinach and avocado, a cup of unsweetened coffee or tea |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, avocado, and a vinaigrette dressing |
| Dinner | Salmon with roasted broccoli and cauliflower |
| Snacks | Handful of almonds, keto-friendly protein bar, or a slice of cheese |
Keto-Friendly Foods
Here is a list of keto-friendly foods categorized by food groups:
Protein Sources
- Meat: Beef, chicken, pork, lamb, turkey
- Fish and Seafood: Salmon, tuna, shrimp, crab
- Eggs
- Dairy: Cheese, yogurt (full-fat and unsweetened)
- Tofu and Tempeh
Healthy Fats
- Olive oil
- Avocado oil
- Coconut oil
- Butter and ghee
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds
- Avocados
Low-Carb Vegetables
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, lettuce
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Asparagus
- Bell peppers
- Mushrooms
- Brussel sprouts
Keto-Friendly Snacks
- Nuts and seeds
- Cheese
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Keto-friendly protein bars
- Avocado slices
- Olives
Tips for Meal Planning and Grocery Shopping
- Plan your meals in advance: This will help you avoid impulsive choices and ensure you have the necessary ingredients on hand.
- Create a shopping list: This will help you stay focused and avoid buying unnecessary items.
- Read food labels carefully: Pay attention to the carbohydrate content of all foods, especially processed foods.
- Stock up on keto-friendly staples: This includes protein sources, healthy fats, and low-carb vegetables.
- Don’t be afraid to experiment: There are countless delicious and healthy keto-friendly recipes available online and in cookbooks.
- Prepare meals in advance: This can save you time and effort during the week.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential on the keto diet, as it helps to flush out ketones and prevent dehydration.
Keto Diet for Weight Loss
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, has gained popularity as a weight loss strategy. It involves drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with fat, forcing the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. In this state, the body primarily burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
How the Keto Diet Contributes to Weight Loss
The keto diet can contribute to weight loss through several mechanisms:
- Reduced Appetite: The keto diet can lead to a decrease in appetite and hunger. This is because ketones, the primary energy source in ketosis, are more satiating than glucose, the primary energy source when consuming carbohydrates. Studies have shown that individuals on a keto diet experience a significant reduction in hunger and calorie intake, leading to weight loss.
- Increased Satiety: High-fat foods, a staple of the keto diet, are known to increase satiety. Fat takes longer to digest than carbohydrates, leading to a feeling of fullness and reducing the urge to overeat.
- Boosting Metabolism: While the keto diet does not directly increase metabolism, it can contribute to a slight boost. The process of converting fat into ketones requires more energy than converting carbohydrates, leading to a slightly higher metabolic rate.
Role of Calorie Restriction and Physical Activity
While the keto diet can contribute to weight loss, it’s essential to remember that calorie restriction remains crucial. The keto diet does not magically burn fat; it simply provides an alternative fuel source. If you consume more calories than you burn, you will not lose weight, regardless of the diet you follow.
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in weight management. It helps burn calories, build muscle mass, and improve overall health. Incorporating exercise into your routine alongside the keto diet can significantly enhance weight loss results.
Tips for Sustainable Weight Loss on a Ketogenic Diet
Sustaining weight loss on the keto diet requires a holistic approach that goes beyond just dietary changes. Here are some tips:
- Gradual Transition: Avoid drastic changes to your diet. Start by gradually reducing carbohydrates and increasing healthy fats. This allows your body to adjust to the new fuel source and minimizes potential side effects.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods like leafy greens, non-starchy vegetables, meat, poultry, fish, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and artificial sweeteners.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Dehydration can mimic hunger and make it difficult to stay on track with your diet.
- Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Eat slowly and savor your meals. This can help you avoid overeating and promote better digestion.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting the keto diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. They can provide personalized advice and ensure the diet is safe and appropriate for you.
Keto Diet for Athletes
The ketogenic diet, with its emphasis on fat and low carbohydrates, has gained popularity among athletes seeking to improve performance and recovery. While it offers potential benefits, it’s crucial to understand its impact on athletic performance and the adjustments required for successful implementation.
Impact on Performance and Endurance
The ketogenic diet’s impact on athletic performance is a subject of ongoing research, with mixed findings. While some athletes report improved endurance and reduced fatigue, others experience a decline in performance, particularly in high-intensity activities.
The potential benefits of the ketogenic diet for athletes include:
- Increased fat oxidation: The ketogenic diet promotes the body’s ability to utilize fat as a primary energy source, potentially enhancing endurance during prolonged exercise.
- Reduced muscle soreness: Some studies suggest that the ketogenic diet may help reduce muscle soreness and inflammation after exercise, leading to faster recovery.
- Improved mental clarity: The ketogenic diet’s effects on brain function, such as increased ketone production, may lead to enhanced cognitive function and mental focus, which can be beneficial for athletes.
However, potential drawbacks include:
- Reduced glycogen stores: The ketogenic diet restricts carbohydrate intake, which limits glycogen stores, the body’s primary energy source for high-intensity exercise. This can result in a decrease in power output and anaerobic capacity, leading to a decline in performance in short-burst activities.
- Slower recovery: The body’s reliance on fat as fuel during the ketogenic diet may result in slower recovery after intense exercise, as it takes longer to replenish fat stores compared to glycogen.
- Dehydration: The ketogenic diet can lead to increased water loss through urination, potentially causing dehydration, which can negatively impact performance.
Adapting Training and Nutrition Strategies
Athletes considering the ketogenic diet need to adapt their training and nutrition strategies to optimize performance:
- Gradual adaptation: Transitioning to a ketogenic diet should be gradual to allow the body to adapt to using fat as a primary fuel source. This may involve a gradual reduction in carbohydrate intake over several weeks.
- Carb cycling: Some athletes find that incorporating periods of higher carbohydrate intake, known as carb cycling, can improve performance and recovery. This involves strategically increasing carbohydrate intake during training cycles or before specific competitions to replenish glycogen stores.
- Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial on the ketogenic diet. Athletes should consume sufficient water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, to prevent dehydration.
- Electrolyte supplementation: The ketogenic diet can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly sodium and potassium loss. Athletes may need to supplement with electrolytes to prevent cramps, fatigue, and other side effects.
- Timing of meals: Timing meals around training sessions is essential for optimal performance. Athletes should consume a high-fat meal or snack several hours before exercise to ensure adequate fat availability for energy.
- Training intensity: Athletes may need to adjust training intensity and duration during the initial adaptation phase of the ketogenic diet, as performance may be affected.
Examples of Successful Athletes
Several athletes have successfully incorporated the ketogenic diet into their training regimens, including:
- Tim Ferriss: The author and entrepreneur has advocated for the ketogenic diet and its benefits for athletic performance.
- Tom Brady: The legendary quarterback has reportedly followed a ketogenic diet, crediting it for improved performance and recovery.
- LeBron James: The NBA superstar has experimented with the ketogenic diet, citing its potential benefits for weight management and overall health.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples, and individual results may vary. The ketogenic diet’s effectiveness for athletes depends on various factors, including individual physiology, training goals, and adherence to the diet.
Myths and Misconceptions about the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet, a popular weight loss approach, has garnered significant attention. However, alongside its popularity, a number of misconceptions and myths have emerged, leading to confusion and misinformation. This section aims to debunk these myths and provide a balanced understanding of the keto diet.
The Keto Diet is Unhealthy
A common misconception is that the keto diet is inherently unhealthy. While it’s true that restricting entire food groups can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned, a well-designed keto diet can be nutritionally balanced. It’s crucial to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, healthy fats, and lean protein while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
A well-designed keto diet emphasizes nutrient-rich foods, ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals.
The Keto Diet is Unsustainable
Another misconception is that the keto diet is unsustainable in the long term. While it’s true that some individuals may find it challenging to maintain strict adherence to the diet over extended periods, this is not necessarily a characteristic of the keto diet itself. Many individuals successfully maintain a ketogenic lifestyle for years, incorporating it into their long-term health goals.
Long-term adherence to the keto diet depends on individual preferences, lifestyle factors, and proper planning.
The Keto Diet Causes Nutrient Deficiencies
While the keto diet can potentially lead to nutrient deficiencies if not planned carefully, this is not an inevitable consequence. A well-designed keto diet emphasizes nutrient-rich foods, ensuring adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals. It’s crucial to include a variety of vegetables, healthy fats, and lean protein sources in the diet.
Nutrient deficiencies are preventable through careful planning and incorporating a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods.
The Keto Diet Leads to Long-Term Health Risks
There is limited evidence to suggest that a well-designed keto diet leads to long-term health risks. However, it’s important to note that long-term studies on the keto diet are limited. As with any dietary approach, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs and goals.
While long-term studies are limited, a well-designed keto diet does not appear to pose significant long-term health risks.
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet is a popular dietary approach that has gained significant attention for its potential benefits in weight loss, metabolic health, and cognitive function. However, it is essential to approach this diet with caution and understanding.
The ketogenic diet, characterized by its high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate intake, forces the body to enter a state of ketosis, where it primarily uses fat for energy instead of glucose. While this metabolic shift can lead to various benefits, including weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity, it is crucial to recognize that the ketogenic diet is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Individualized Approach
The effectiveness and safety of the ketogenic diet can vary greatly from person to person. It is imperative to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a ketogenic diet to determine if it is suitable for your individual needs and health conditions. A healthcare professional can help you assess your health status, monitor potential side effects, and tailor the diet to your specific requirements.
Furthermore, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with the ketogenic diet, such as nutrient deficiencies, digestive issues, and kidney stones. These risks can be minimized by following a well-balanced ketogenic diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods and by staying adequately hydrated.
Further Exploration
The ketogenic diet is a complex and evolving area of research. Ongoing studies continue to explore its long-term effects and potential benefits and risks. It is important to stay informed about the latest scientific findings and to make informed decisions based on reliable and evidence-based information.
Remember, the ketogenic diet should not be viewed as a quick fix or a magic bullet. It requires a significant commitment to lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular exercise. With careful planning, monitoring, and guidance from a healthcare professional, the ketogenic diet can be a valuable tool for achieving specific health goals.
Final Summary
The keto diet is a complex and often controversial dietary approach that can be a powerful tool for achieving specific health goals. While it can offer benefits for weight loss, blood sugar control, and even certain medical conditions, it’s crucial to understand its potential risks and side effects. Before embarking on a ketogenic journey, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your individual needs and health status. With proper guidance and a balanced approach, the keto diet can be a valuable tool for improving your overall well-being.
Query Resolution
Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
The keto diet may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with pre-existing medical conditions. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a keto diet, particularly if you have diabetes, kidney disease, or other health concerns.
How long does it take to enter ketosis?
The time it takes to enter ketosis can vary depending on individual factors like metabolism, previous diet, and activity level. Most people experience ketosis within 2-7 days of starting a keto diet.
What are some common side effects of the keto diet?
Common side effects of the keto diet include “keto flu” (headache, fatigue, nausea), constipation, nutrient deficiencies, and electrolyte imbalances. These side effects usually subside within a few days to a week as your body adapts.
Can I exercise on a keto diet?
Yes, you can exercise on a keto diet. However, it’s important to adjust your training intensity and fuel intake to account for the changes in your body’s energy source. Consulting with a fitness professional can help you tailor your workout routine to a ketogenic lifestyle.
The keto diet, which focuses on high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate intake, forces your body to burn fat for energy instead of glucose. This process, called ketosis, can be a bit tricky to navigate, especially when it comes to beverages.
You might wonder, can you drink diet soda on keto ? While diet soda is technically low in carbs, some argue it can interfere with ketosis by triggering insulin spikes. Ultimately, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine what works best for your individual needs and goals on the keto diet.
The keto diet works by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, forcing your body to burn fat for energy instead of glucose. This process, known as ketosis, can lead to weight loss and other health benefits. However, some people find it challenging to maintain a keto diet long-term.
If you’re looking for a different approach, you might be interested in learning about how does golo diet work , which focuses on managing insulin levels and promoting healthy metabolism. Ultimately, the best diet for you depends on your individual needs and preferences.
The keto diet works by forcing your body to burn fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This happens when you drastically reduce your carb intake, leading to a state called ketosis. While this dietary approach can be effective for weight loss, it’s crucial to remember that diet alone isn’t always the answer.
Exercise plays a significant role in achieving your weight loss goals, and you might wonder if running is the most effective way to do so. Is running the best way to lose weight ? Ultimately, the effectiveness of any weight loss strategy depends on your individual needs and preferences, and combining a keto diet with a regular exercise routine can be a powerful combination.